Pharmaceutical packaging is a critical aspect of the industry, ensuring the protection, preservation, and safe delivery of medications. Induction cap sealing is a widely used method in pharmaceutical packaging, offering a reliable way to seal containers and protect the contents from tampering, contamination, and other external factors.
Pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals and OTC medicines all need to be sealed securely, with tamper evidence and easy opening. These products may travel across long supply chains, from manufacturing to consumers.
Induction cap sealing is a process that involves the use of electromagnetic induction to create a hermetic seal between a container and its closure. It is commonly used for sealing bottles, jars, and other containers in the pharmaceutical industry. This sealing method provides an effective barrier against moisture, gases, and other contaminants, thereby ensuring the integrity and safety of the packaged products.
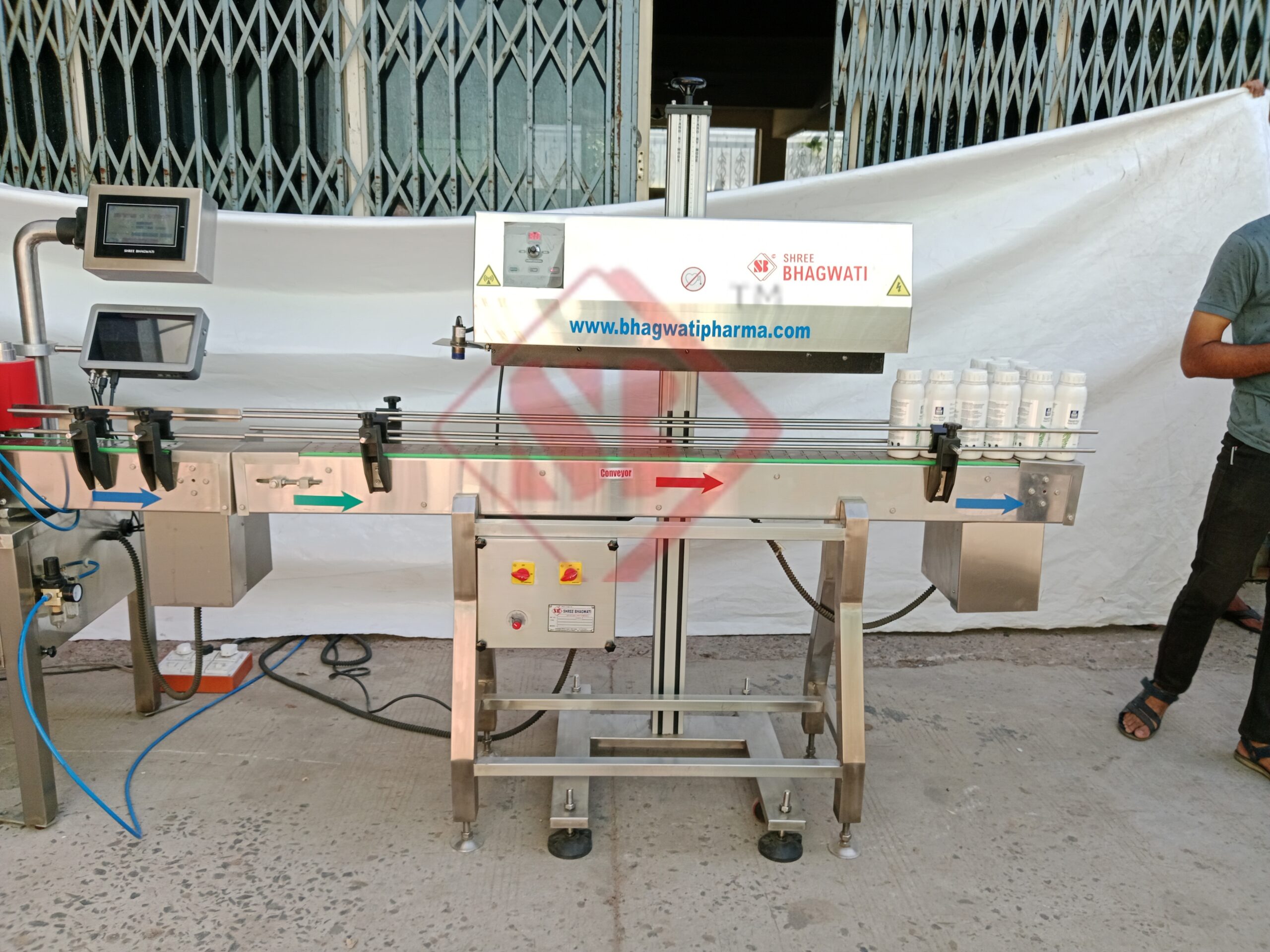
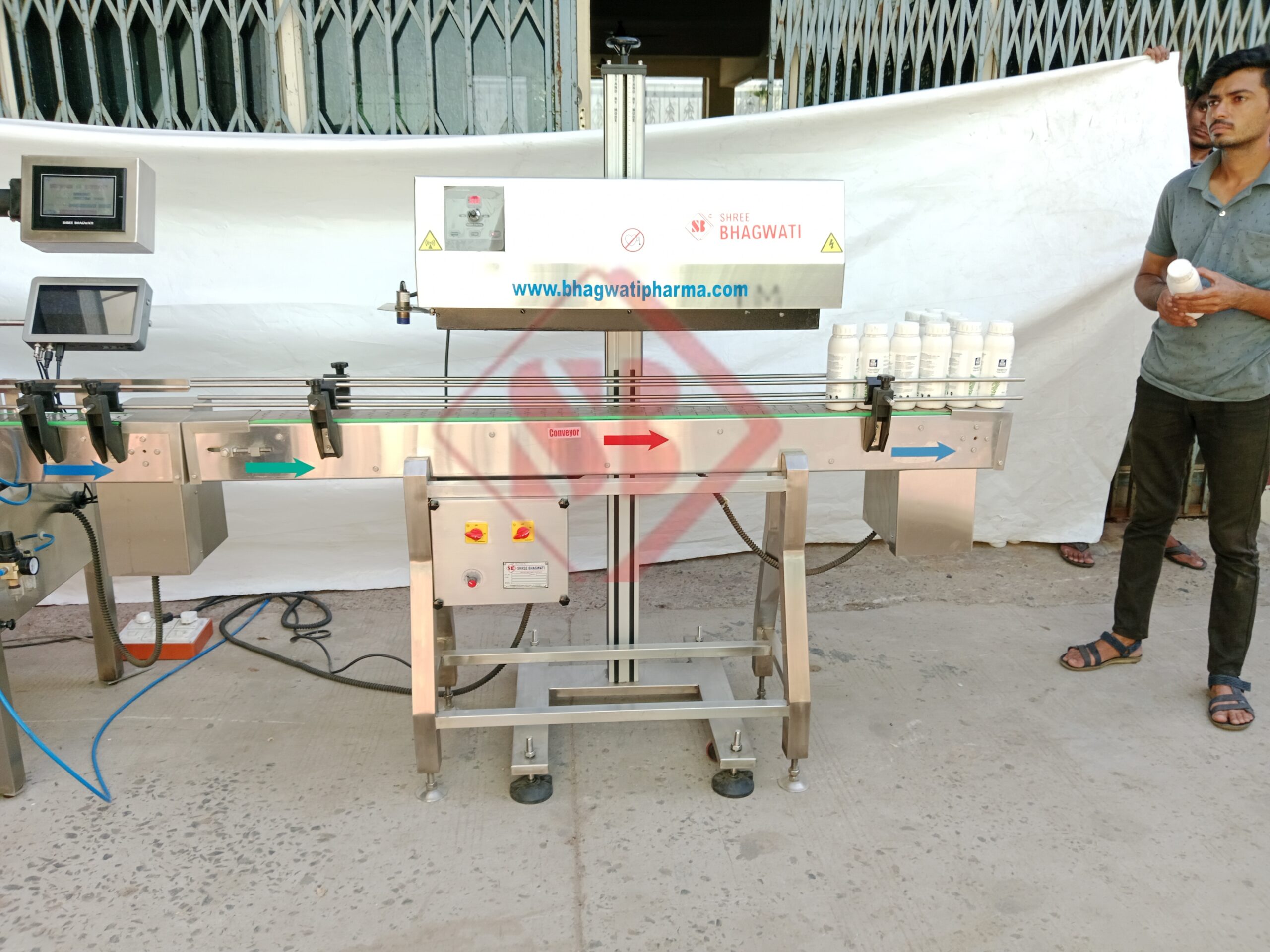

How Does Induction Cap Sealing Work?
The induction cap sealing process involves three key components: a closure with a foil liner, an induction sealing machine, and a heat source. The closure is typically made of materials such as aluminum or plastic and contains a foil liner. The liner is coated with a heat-sealable material that bonds to the container’s rim when exposed to heat.
During the sealing process, the closure is placed on the container, and the induction sealing machine generates an electromagnetic field. The closure, with its foil liner, is passed through this field, which induces electrical currents in the foil. These currents generate heat, causing the heat-sealable material on the liner to melt and bond with the container’s rim. As a result, a secure and tamper-evident seal is formed, providing protection against unauthorized access and product tampering.
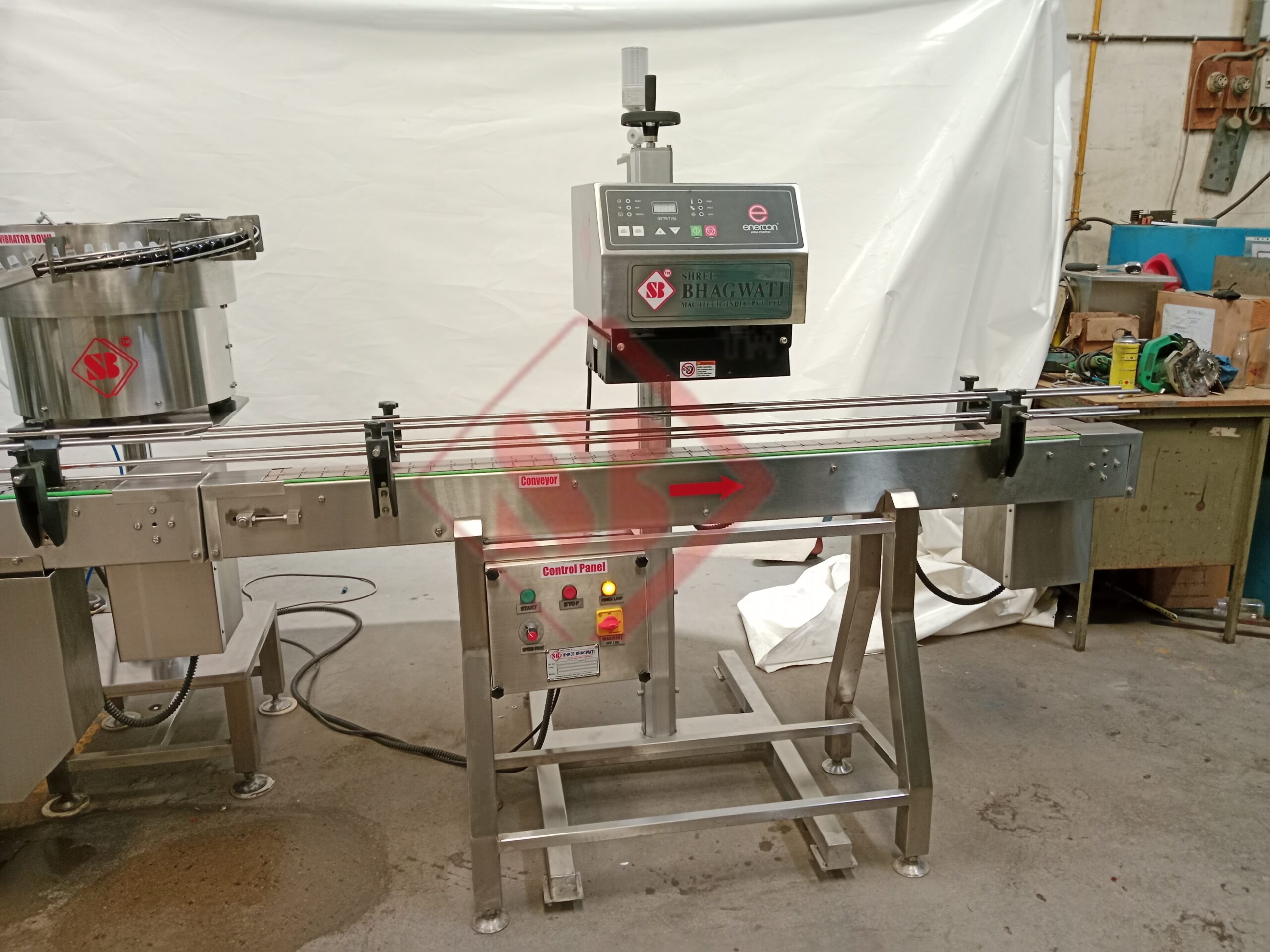
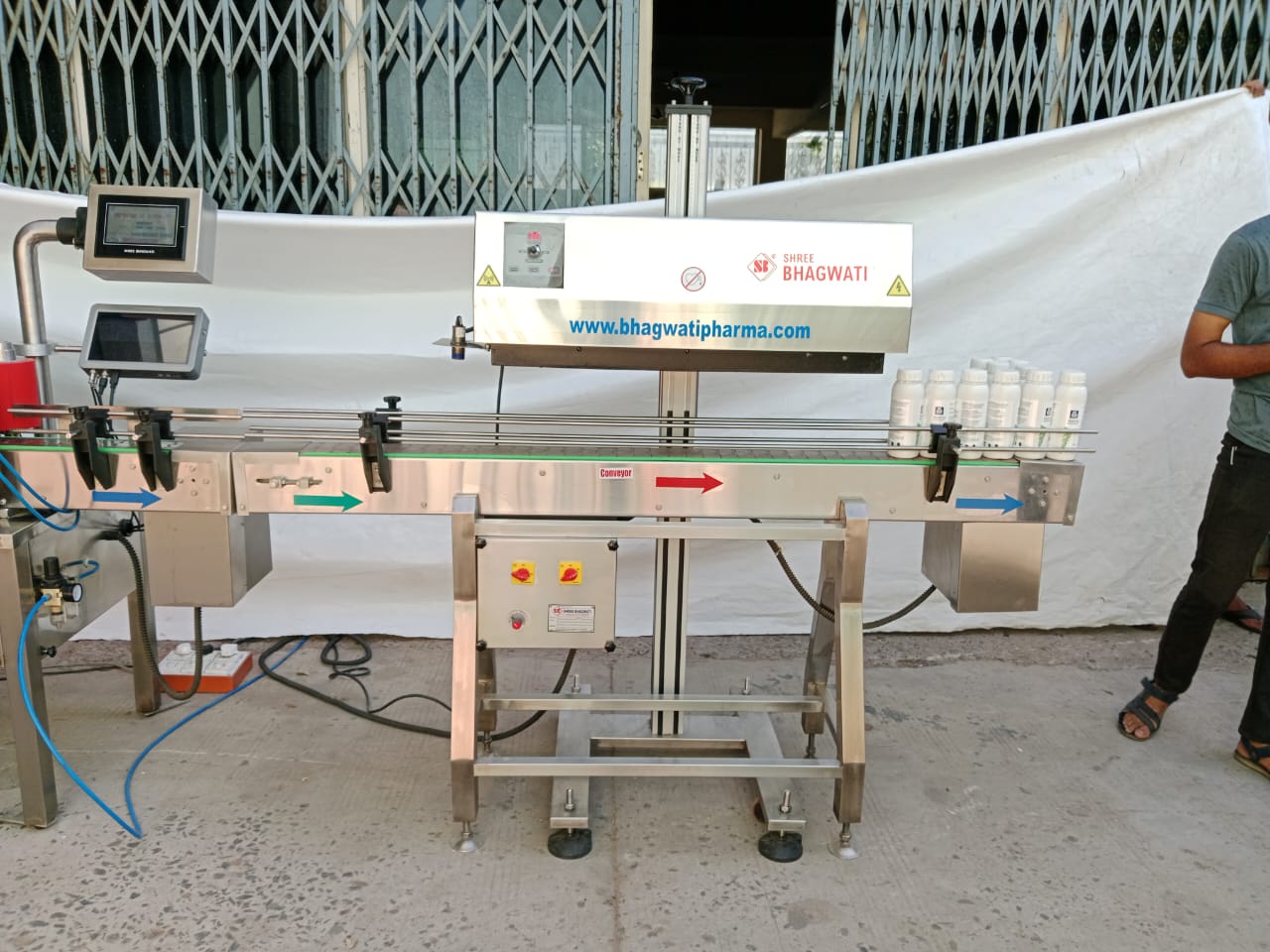


Importance of Induction Cap Sealing in Pharmaceutical Packaging
Induction cap sealing plays a crucial role in ensuring consumer safety in pharmaceutical packaging. By providing a hermetic seal, it prevents the entry of moisture, oxygen, and other contaminants that could compromise the quality and efficacy of medications. This sealing method also acts as a tamper-evident feature, enabling consumers to identify if a product has been previously opened or tampered with.
In the pharmaceutical industry, where product integrity and patient safety are paramount, induction cap sealing provides a reliable solution to protect medications from external influences. It helps to extend the shelf life of pharmaceutical products, maintain their potency, and reduce the risk of contamination, ensuring that consumers receive medications that are safe and effective.
Benefits of Induction Cap Sealing
Induction cap sealing offers several benefits that make it a preferred choice in pharmaceutical packaging:
a. Tamper-evidence:
Induction cap sealing provides a visible and reliable indication of tampering. Any attempt to open the container without breaking the seal will be evident, alerting consumers to potential product tampering.
b. Product Integrity:
The hermetic seal created by induction cap sealing prevents the entry of moisture, oxygen, and other contaminants. This helps to maintain the integrity and stability of pharmaceutical products, ensuring their quality and efficacy over an extended period.
c. Extended Shelf Life:
By offering superior protection against external factors, induction cap sealing helps to extend the shelf life of pharmaceutical products. This is particularly important for medications that have a longer lifespan or require storage over an extended period.
d. Brand Protection:
Induction cap sealing can be customized with branding elements, including logos and security features. This helps to enhance brand recognition and protect against counterfeiting, safeguarding the reputation of pharmaceutical companies.