Sticker labeling machines are essential equipment used in various industries for applying labels onto products efficiently and accurately. Two primary technologies used in these machines are pressure-sensitive labeling and glue-based labeling. This article provides a comparative analysis of these two systems.
Introduction to Sticker Labeling Machines
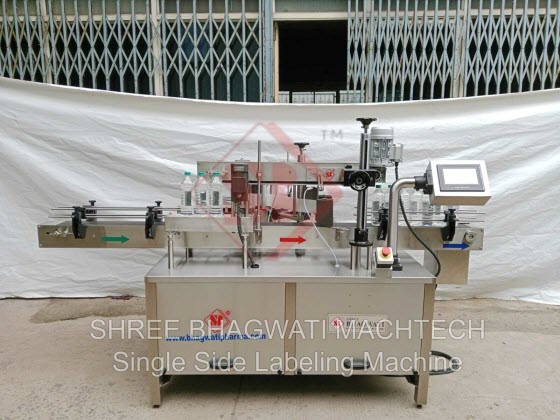
Sticker labeling machines are automated devices designed to apply labels onto products, containers, or packages. These machines streamline the labeling process, improve productivity, and ensure consistent label placement and quality.


Pressure-Sensitive Labeling Technology
Operation Mechanism
Pressure-sensitive labeling technology utilizes adhesive-backed labels that adhere to the surface of the product when pressure is applied. The labels are typically fed through a labeling head, where they are dispensed onto the product and pressed firmly into place using rollers or belts.
Advantages
- Versatility: Pressure-sensitive labels can adhere to a wide range of surfaces, including glass, plastic, metal, and paper.
- No Drying Time: Unlike glue-based systems, pressure-sensitive labels do not require drying time, allowing for faster production speeds.
- Easy Changeover: Switching between different label designs or sizes is relatively quick and straightforward with pressure-sensitive labeling machines.
Limitations
- Cost: Pressure-sensitive labels may be more expensive than glue-applied labels, especially for custom or specialty designs.
- Adhesive Residue: Residual adhesive left on the machine components may require frequent cleaning to prevent buildup and maintenance issues.


Glue-Based Labeling Technology
Operation Mechanism
Glue-based labeling technology relies on applying adhesive to the back of labels before they are dispensed onto the product. The adhesive can be applied using various methods, including hot melt glue, cold glue, or wet glue systems.
Advantages
- Cost-Effectiveness: Glue-based labels are often less expensive than pressure-sensitive labels, making them a preferred choice for high-volume production.
- Durability: Glue-based labels typically offer stronger adhesion and resistance to moisture, heat, and other environmental factors.
- Minimal Residue: Glue-based systems may produce less adhesive residue buildup on machine components compared to pressure-sensitive systems.
Limitations
- Drying Time: Glue-based labels require time to dry and set properly, which can slow down production speeds compared to pressure-sensitive systems.
- Limited Surface Compatibility: Some surfaces may not be suitable for glue-based labels, particularly those with irregular shapes or textures.

Comparison of Pressure-Sensitive and Glue-Based Systems
Cost Considerations
Pressure-sensitive labeling machines may have higher upfront costs due to the need for specialized label materials and applicators. However, they may offer lower ongoing costs in terms of maintenance and material waste. Glue-based systems may have lower upfront costs but may incur higher expenses for adhesive materials and maintenance over time.
Application Versatility
Pressure-sensitive labeling machines are more versatile in terms of label material compatibility and surface adhesion. They can handle a wider range of label designs and substrates, making them suitable for diverse packaging requirements. Glue-based systems may be more limited in their application due to the specific adhesive requirements and surface compatibility issues.
Speed and Efficiency
Pressure-sensitive labeling machines generally offer faster production speeds and shorter changeover times compared to glue-based systems. The absence of drying time allows for continuous operation and higher throughput rates. Glue-based systems may require longer setup and downtime for adhesive application and drying processes, resulting in slower overall production speeds.
Maintenance Requirements
Pressure-sensitive labeling machines may require more frequent cleaning and maintenance to remove adhesive residue buildup and ensure smooth operation. Glue-based systems may have lower maintenance requirements in terms of adhesive application components but may require periodic cleaning and adjustment of glue application systems.
Industry Applications
Both pressure-sensitive and glue-based labeling technologies find applications across various industries, including:
- Food and Beverage: Packaging of food products such as bottles, cans, and containers.
- Pharmaceutical: Labeling of pharmaceutical bottles, vials, and packaging.
- Personal Care: Labeling of cosmetic containers, tubes, and packaging.


Future Trends
Automation
Continued advancements in automation technologies are expected to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of sticker labeling machines. Integration with robotic systems and artificial intelligence (AI) will enable autonomous operation and real-time monitoring of labeling processes.
Integration with IoT
Sticker labeling machines may be integrated with Internet of Things (IoT) platforms to enable remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven insights. IoT-enabled systems can optimize machine performance, minimize downtime, and improve overall productivity.
Sustainable Labeling Solutions
Future developments in labeling technologies will focus on eco-friendly materials and processes to reduce environmental impact. Biodegradable label materials, recyclable adhesives, and energy-efficient labeling systems will become increasingly prevalent to meet sustainability goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both pressure-sensitive and glue-based labeling technologies offer distinct advantages and limitations depending on the specific requirements of the application. Pressure-sensitive systems excel in versatility, speed, and ease of use, while glue-based systems offer cost-effectiveness, durability, and compatibility with certain packaging materials. Understanding the differences between these technologies is crucial for selecting the most suitable labeling solution for each application.